Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall wellness, and it all comes down to a balance of good bacteria in your gut. You’ve likely heard about probiotics and prebiotics, but understanding how they work together can help you make better choices for your gut health. In this blog, we’ll explore how probiotics and prebiotics work together, their sources, and their role in supporting your immune system and digestive health.
What Are Probiotics

Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that reside in your gut, playing a vital role in maintaining a healthy gut. These bacteria help balance your gut microbiome, aiding in digestion and supporting your immune system. Common sources of probiotics include foods like yogurt, kefir, and other fermented foods. Additionally, probiotic supplements are widely available and are often used to help maintain a healthy gut environment, especially when dietary sources are limited.
What Are Prebiotics?
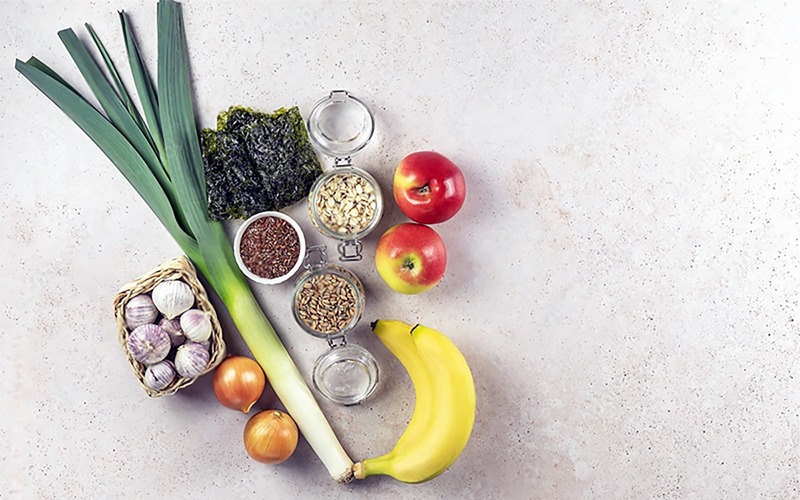

Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that act as a food source for the beneficial bacteria in your gut. Unlike probiotics, prebiotics are not live bacteria; instead, they are found in various plant-based foods such as onions, garlic, bananas, oats, and asparagus. By consuming prebiotic foods, you provide nourishment to the good bacteria, allowing them to thrive and perform their vital functions in your gut. This helps enhance the overall environment of your gut microbiome, aiding in healthy digestion.
How Probiotics and Prebiotics Work Together
The relationship between probiotics and prebiotics can be likened to a garden. Probiotics are like the plants in the garden—live organisms that need to grow and thrive—while prebiotics are the fertilizer that nourishes these plants. Together, they create a balanced environment that helps maintain gut health.
“Probiotics Need Prebiotics to Thrive”
Probiotics need a constant food source to survive and multiply. Prebiotics serve as this food source, providing the necessary nutrients that probiotics need to grow. When you consume prebiotic-rich foods, you help enhance the growth of beneficial bacteria, ensuring that your gut remains balanced and functioning well.
Sources of Probiotics and Prebiotics

To harness the benefits of probiotics and prebiotics, incorporating them into your diet through foods or supplements is essential. Below are some common sources:
- Probiotic Sources:
Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, and probiotic supplements. - Prebiotic Food Sources:
Onions, garlic, leeks, asparagus, bananas, oats, and whole grains.
Prebiotic & Probiotic Supplements: When Should You Consider Them?

While many people can get enough pre & probiotics from food, supplements can be a convenient option, especially for those who have dietary restrictions or prefer a more controlled intake. Probiotic supplements contain specific strains of bacteria that can target particular health needs, helping maintain a healthy gut environment.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Probiotics and prebiotics are generally safe for most people, but they can sometimes cause mild digestive side effects like bloating or gas, especially when starting out. It’s always a good idea to start with small amounts of probiotic and prebiotic foods or supplements and gradually increase as your body adapts.
For those with certain health conditions, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting probiotic supplements to ensure they are appropriate for your individual health needs.
Conclusion
Probiotics and prebiotics work hand-in-hand to support a healthy gut, contributing to better digestion, enhanced immune function, and overall well-being. By incorporating a variety of probiotic-rich foods and prebiotic food sources into your diet, you can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome. Whether you choose foods or supplements, understanding the unique roles that these components play can guide you toward better gut health and a healthier you.